A child with school avoidance may qualify for an Individualized Education Plan governed by the U.S. Federal Law, the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA).
IDEA guarantees each child with a disability and in need of special education services the right to a free and appropriate public education (FAPE) in the least restrictive environment (LRE).

Interpreting How IDEA Defines “Educational Performance” to Qualify for An Individualized Educations Plan (IEP)
Because the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act does not explain the intent of the language “Educational Performance”, school administrators will differ in their interpretations of the law. In order to provide clarity to see how a child with school avoidance may qualify for an IEP we will share legal analysis from the Campbell Law Journal.
They first discuss that IDEA uses the word “educational” and is opposed to the narrower definition of “academic.”
The plain meaning of the word “educational” seems to reference not only academic learning, but also social, emotional, and interpersonal development. The theme underlying both the definitions and the etymological origins is one of equipping an individual with a variety of skills and preparing him/her for “mature” or independent life. This same theme is mirrored in the purpose statements in the IDEA. “Academic” is a narrower term referencing specific aspects of education pertaining to school, higher learning, courses, and formal study.
Jamie Lynne Thomas, Decoding Eligibility Under the IDEA: Interpretations of “Adversely Affect Educational Performance”, 38 Campbell L. Rev. 73 (2016). Tweet
Furthermore, the regulations require use of a “variety of assessment tools and strategies to gather relevant functional, developmental, and academic information about the child” to assist in determining whether the child is a child with a disability. It specifically rejects the use of “any single measure or assessment as the sole criterion” for making this determination. These aspects of the regulations further support the broader interpretation of the word “educational,” especially since “academic information” is one of several types of information that should be considered in this analysis.
Jamie Lynne Thomas, Decoding Eligibility Under the IDEA: Interpretations of “Adversely Affect Educational Performance”, 38 Campbell L. Rev. 73 (2016). Tweet
The terminology “Adversely Affects” also leaves interpretation open to the opinion of the evaluator. So again Attorney Jamie Lynn Thomas helps us clarify the intended definition under the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA). She refers to guidance from the Office of Special Education Programs in the US Department of Education to provide analysis.
“It must be determined on a case-by-case basis, depending on the unique needs of the particular child and not based only on discrepancies in age or grade performance in academic subject areas.
A child may qualify as a child with a disability in need of special education and related service even though the child has not failed or been retained in a course or grade, and is advancing from grade to grade.”The Office of Special Education Programs, The United States Department of Education Tweet
The least restrictive environment (LRE) is essential to ensure all kids, regardless of their disability (can be a mental health disorder or learning difference), are given the exact same opportunities as any other kid to enjoy every aspect of the school experience; from academics to socialization.
LRE will come into play with each interventional assistance you request for your child. Most schools will use this appropriately, but because school avoidance is sometimes misunderstood, LRE can also be used as an excuse why your child cannot receive a 504 plan, IEP, or Out of District Placement (OOD).
Their thinking may be child-centric, and they may be concerned about the child not living in his own home with parents and siblings. And living far from local friends.
Also, it’s possible your school doesn’t want to pay for this expensive placement and won’t consider it, using LRE as the reason.
The words Special Education may give the impression that this only refers to children with physical or intellectual challenges, but it encompasses other characteristics and criteria that may include and be able to help a child with school avoidance.
The Special Education (Special Services) department at your school is where the Child Study Team works. They report to the Director of Special Services (Special Education) in your school district.
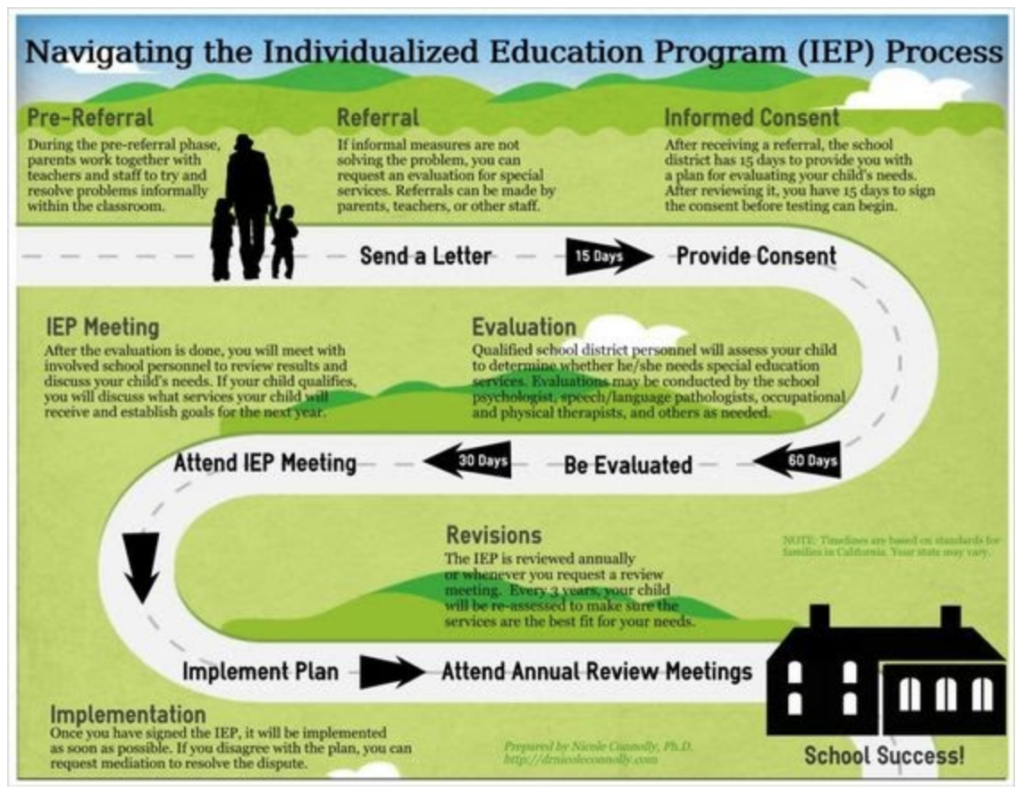
They are your contacts to request an evaluation for your child to be considered for an Individualized Education Plan (IEP, Special Education)
You, as an advocate, must make the determination as to the level of assistance, accommodations, modifications, and services that your child needs in order to get your child with school avoidance back into school.
As we discussed above, In order to qualify for an IEP, a student must be found to have one of the 13 Characteristics of special education (below) and it must adversely affect their educational performance.
According to Sec. 300.101 (a) of IDEA, “A free appropriate public education must be available to all children residing in the State between the ages of 3 and 21, inclusive, including children with disabilities who have been suspended or expelled from school, as provided for in §300.530(d).
Many kids with school avoidance suffer from a mental health disability or learning disability.
You may need a special education designation for your child in order to get the appropriate program and accommodations for your child.
*IDEA defines an emotional regulation impairment that qualifies for special education as the following:
A condition exhibiting one or more of the following characteristics over a long period of time into a marked degree that “ADVERSELY AFFECTS”* a child’s educational performance:
A. An inability to learn that cannot be explained by intellectual, sensory, or health factors.
B. An inability to build or maintain satisfactory interpersonal relationships with peers and teachers.
C. Inappropriate types of behavior or feelings under normal circumstances.
D. A general pervasive mood of unhappiness or depression.
E. A tendency to develop physical symptoms or fears associated with personal or school problems.
Click here if you want to read the exact statutes on IDEA as provided by the U.S. Department of Education:
If your child does not qualify for services under IDEA, they may be eligible for modifications under Section 504 of the American Disabilities Act of 1973.
Disclaimer: This site is designed by School Avoidance Alliance to assist parents, family, friends, caregivers, educators, advocates, and other professionals involved with helping children and finding resources to understand, help and cope with school avoidance, as well as to increase public awareness regarding school avoidance. The contents of this website are presented for informational and educational purposes only. Nothing on this website is to be construed as professional advice on medical, legal, technical, or therapeutic matters. By accessing and using the information on this site, you agree to waive any rights to hold the site developer(s), or any individual and/or group associated with this site, liable for any damage that may result from the use of the information presented.
Unfortunately only a small percentage of school professionals, therapists, educational advocates and policy makers understand school avoidance best practices. So, you must become the expert to ensure your child is getting:
The time passing slowly without progress is the worst feeling. It wouldn’t have taken five years of suffering and uncertainty if I had this expert guidance during my son’s school avoidance. We would have saved $29,000 in lawyer fees and $69,000 for private schools.
